Businesses often find themselves heavily dependent on technology, data, and communication systems. With this comes the urgent need for robust security measures that can shield valuable assets from a multitude of threats. To effectively safeguard these assets, it is crucial to recognize and address the unique challenges of internal security threats.
Recently, the WinZip® Enterprise team has undertaken a comprehensive survey, shedding light on the mounting uncertainty surrounding the increasing number and sophistication of cyber threats.
The survey’s overall findings show how crucial it is for organizations to promptly and efficiently tackle internal data security risks head-on. This article will explore examples of internal security threats and how to avoid them.
Internal security threats and risks for businesses
Internal security threats represent various risks that originate from within an organization itself.
These dangers manifest when individuals with authorized access to sensitive data or systems misuse their privileges, either deliberately or unintentionally. Such threats can arise from employees, contractors, or trusted partners.
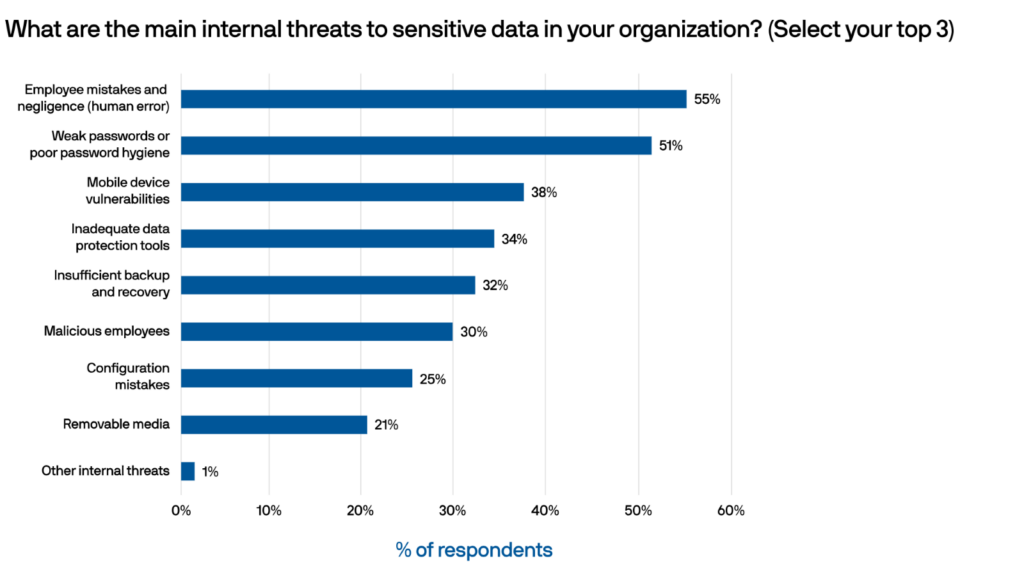
Our survey found that the top internal data security threats reported were employee mistakes and negligence (human error), weak passwords or poor password hygiene, and mobile device vulnerabilities.
Ignoring internal security risks leaves organizations vulnerable to potential financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences, emphasizing the need for comprehensive security measures that address these threats.
Examples of internal security threats (and why they occur)
Internal threats pose significant risks to organizations, making it essential to identify, understand, and address them effectively.
This section explores some of the top internal security threats companies face, according to finding from our survey, provides examples of how they occur, and offers insights into potential solutions.
1. Employee mistake and human error (55%)
Employee mistakes or human errors can present significant internal risks, potentially leading to data breaches, system vulnerabilities, and operational disruptions.
Some examples include employees:
- Falling victim to phishing scams.
- Inadvertently sharing sensitive information with unauthorized individuals.
- Mishandling critical data through improper disposal methods.
Such errors can be mitigated through:
- Comprehensive employee training programs.
- Enforcing robust data handling protocols.
- Implementing strong access controls and monitoring mechanisms.
2. Weak password hygiene (51%)
Weak password hygiene can leave systems vulnerable to unauthorized access or compromise.
Examples of how weak password hygiene can be an internal risk include employees:
- Using easily guessable passwords.
- Sharing passwords with colleagues.
- Reusing the same password across multiple accounts.
These practices increase the likelihood of successful brute-force attacks, unauthorized account access, or credential theft.
To address this risk, organizations should:
- Enforce strong password policies.
- Implement multi-factor authentication.
- Conduct regular employee training on password best practices to promote password hygiene.
3. Mobile device vulnerabilities (38%)
Mobile device vulnerabilities can expose sensitive data and networks to potential breaches and unauthorized access.
Examples of how mobile device vulnerabilities include employees:
- Downloading malicious applications that compromise device security.
- Connecting to unsecured Wi-Fi networks.
- Losing their devices without proper data encryption and remote wipe capabilities.
These vulnerabilities can be mitigated by:
- Implementing mobile device management (MDM) solutions.
- Enforcing security policies for mobile devices.
- Regularly updating operating systems and applications.
- Educating employees about safe mobile device practices.
4. Inadequate data protection (34%)
Inadequate data protection can leave sensitive information susceptible to unauthorized access, breaches, and regulatory non-compliance.
Examples of how inadequate data protection can play out include:
- Insufficient encryption of sensitive data.
- Lack of access controls and permissions.
- Inadequate backup and disaster recovery plans.
- Poor data handling practices, such as leaving confidential documents unsecured or sharing them through unencrypted channels.
These risks can be eliminated by implementing robust data protection measures, including:
- Encryption technologies.
- Access controls.
- Regular data backups.
- Employee training on data security protocols.
- Compliance with relevant data protection regulations.
5. Insufficient backup and recovery (32%)
Insufficient backup and recovery processes can lead to data loss, prolonged downtime, and potential financial and operational repercussions.
Examples of how insufficient backup and recovery processes can be an internal risk include:
- In the event of a server failure or corruption, critical files may be irretrievably lost, leading to operational disruptions and potential financial loss.
- If data is infiltrated and encrypted by malicious actors and there are no recent backups available, the organization may be forced to pay a ransom or suffer the permanent loss of important data.
- Extended downtime during system outages or natural disasters is common without a backup plan. Here, the company may struggle to resume normal operations promptly, leading to decreased productivity and potential customer dissatisfaction.
To alleviate these risks, organizations should:
- Establish regular and automated backup procedures.
- Implement off-site data storage.
- Regularly test recovery processes.
- Maintain comprehensive disaster recovery plans.
6. Malicious employees (30%)
Malicious employees can jeopardize sensitive data, sabotage systems, or engage in fraudulent activities.
A few examples of how malicious employees can be internal risks include:
- Employees may abuse their authorized access privileges to gain access to confidential information, such as customer data, trade secrets, or financial records, for personal gain or to sell to competitors.
- A disgruntled employee might intentionally delete or alter crucial data, disrupt systems, or introduce malware or viruses into the company’s network.
- An employee may engage in fraudulent activities, such as embezzlement, invoice manipulation, or misappropriation of funds.
To mitigate these risks, organizations should:
- Implement strong access controls and permissions.
- Regularly monitor employee activities.
- Conduct background checks during hiring.
- Coster a positive and transparent work culture.
- Establish clear policies and procedures for reporting suspicious behavior.
7. Configuration mistakes (25%)
Configuration mistakes can lead to vulnerabilities in systems, networks, or applications.
Here are a few examples of how configuration mistakes can be internal risks:
- Granting excessive privileges or failing to revoke access for employees who have left the company can expose critical resources to potential breaches.
- Failure to properly configure security settings, such as firewall rules, encryption protocols, or intrusion detection systems, can create gaps in a company’s defense mechanisms. This may allow cyber attackers to exploit vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to systems or networks.
- Neglecting to enforce strong password policies, such as requiring complex passwords or regularly changing them, can lead to an increased risk of unauthorized access. Weak passwords or default credentials can be easily exploited by attackers.
To avoid these risks, organizations should:
- Implement robust configuration management practices.
- Conduct regular security audits.
- Perform vulnerability assessments.
- Establish a process for reviewing and validating configurations.
8. Removable media (21%)
Removable media, such as USB or external hard drives, can introduce internal risks within a company if not handled properly.
Examples of how removable media can be a risk to businesses include:
- When employees use removable media devices without proper scanning or security measures, they can unknowingly introduce malware or viruses into the company’s systems. Malicious code can spread quickly and compromise sensitive data or disrupt operations.
- Employees may copy sensitive or confidential company information onto removable media devices to share or sell outside the organization. This can lead to data breaches, intellectual property theft, or compromise of trade secrets.
- Misplacing or losing removable media devices that contain sensitive data can result in potential data loss or leakage.
To stay clear of these issues, organizations should establish clear policies and guidelines regarding the use of removable media devices. This includes:
- Implementing security measures such as encryption for sensitive data.
- Disabling auto-run features.
- Regularly scanning media devices for malware.
- Restricting or monitoring the use of removable media based on business needs.

What should you look for when mitigating internal threats?
When it comes to avoiding internal threats, businesses must adopt proactive measures to protect their sensitive data and systems. Here are some important factors that organizations should consider:
Access controls and privilege management
Implement strong access controls and privilege management protocols to ensure employees have appropriate access rights based on their roles and responsibilities.
Regularly review and revoke access privileges for employees who no longer require them.
Employee education and awareness
Promote a culture of security awareness and provide comprehensive training to employees on internal threats, best practices for data handling, and the importance of reporting suspicious activities.
Encourage employees to follow security protocols and reinforce the significance of maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of company data.
Monitoring and auditing
Implement robust monitoring and auditing mechanisms to detect unusual activities or potential breaches.
This includes monitoring network traffic, access logs, and user behavior to identify unauthorized access attempts or suspicious actions.
Data protection and encryption
Implement data protection measures, including encryption and secure file-sharing solutions, to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access or data leakage.
Encrypting sensitive data both at rest and in transit adds an extra layer of protection against internal threats.
WinZip Enterprise offers businesses a single solution to address internal threats effectively. With its comprehensive suite of features, WinZip helps organizations respond to the diverse security risks they face.
WinZip empowers businesses to combat external threats by offering advanced encryption capabilities, secure file transfer functionality, and comprehensive data loss prevention measures. With our software, organizations can protect their assets from cyberattacks, unauthorized access, and data leakage caused by external threat actors.
Try it now and learn how to safeguard your organization’s future.
Download our report today to learn more about threats to your data security.








