Password security is paramount for enterprises. This blog will highlight its role in safeguarding sensitive data, mitigating cyber threats, and ensuring business continuity in an increasingly digital landscape.
What is password security?
In a corporate setting, password security refers to implementing practices and measures to protect sensitive information and digital assets. Password security ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of current passwords.
Two kinds of password securities are commonly used in businesses and enterprises:
1. Individual password security
Individual password security involves employees and users creating strong, unique passwords, regularly updating them, and refraining from sharing or reusing them across accounts.
This practice uses multi-factor authentication (MFA) and biometric verification to add an extra layer of protection.
2. Company-wide password security
Company-wide password security involves establishing comprehensive policies and protocols. This includes:
- Enforcing password complexity requirements.
- Implementing password expiration and rotation policies.
- Restricting access to authorized personnel.
- Employing advanced authentication methods (single sign-on (SSO) and identity and access management (IAM) systems).
This practice aims to mitigate risks, prevent unauthorized access, and ensure the organization’s overall cybersecurity posture.
The importance of password security
Today, businesses rely heavily on online platforms for communication, transactions, and data storage. Therefore, the significance of robust password security cannot be overstated.
Having strong passwords at the enterprise level is crucial for several reasons:
- Data protection. Strong passwords safeguard sensitive corporate data, intellectual property, and customer information from unauthorized access and potential breaches.
- Mitigating breaches. Robust passwords make it significantly harder for cybercriminals to breach corporate accounts, reducing the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks.
- Regulatory compliance. Strong password practices often align with industry regulations and compliance standards, helping organizations avoid legal and financial consequences.
- Business continuity. Password security contributes to uninterrupted business operations by preventing unauthorized access that could lead to disruptions.
- Employee accounts. Secure passwords protect employee accounts, preventing unauthorized access to payroll, benefits, and personal information.
- Reputation and trust. Maintaining strong password security enhances an organization’s reputation and customer trust by demonstrating a commitment to data protection.
- Intellectual property. Strong passwords guard valuable intellectual property, trade secrets, and proprietary information from theft or espionage.
- Phishing defense. Strong passwords act as a barrier against phishing attacks, where cybercriminals attempt to steal credentials through deceptive means.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhancement. Strong passwords enhance the effectiveness of MFA, adding an additional layer of protection for critical accounts and systems.
- Vendor and partner security. Robust password practices extend to vendor and partner accounts, preventing unauthorized access that could compromise supply chain integrity.
- Employee accountability. Enforcing strong password policies encourages employees to take responsibility for cybersecurity, fostering a culture of accountability.
- Cost savings. Effective password security reduces the financial impact of data breaches, potential lawsuits, and reputation damage.
Heightened password security isn’t a given at every company. In reality, various factors can contribute to why organizations often overlook password security. These include:
- The complexity of implementing and managing strong password policies.
- Concerns about user convenience and productivity.
- Inadequate awareness of the potential consequences of weak passwords.
- Limited resources, competing cybersecurity priorities.
- Reliance on legacy systems with outdated security measures.
- Insufficient employee training.
Password statistics: The impact of weak security
The WinZip® Enterprise team recently completed a survey that clarified the growing concern of cyber security in business. The study’s conclusive results underscore the importance of organizations taking password security seriously.
The survey looked into the depths of modern-day cyber threats and vulnerabilities that businesses face. One of the many takeaways from the study is the pressing need for organizations to address and rectify their approach to password security.
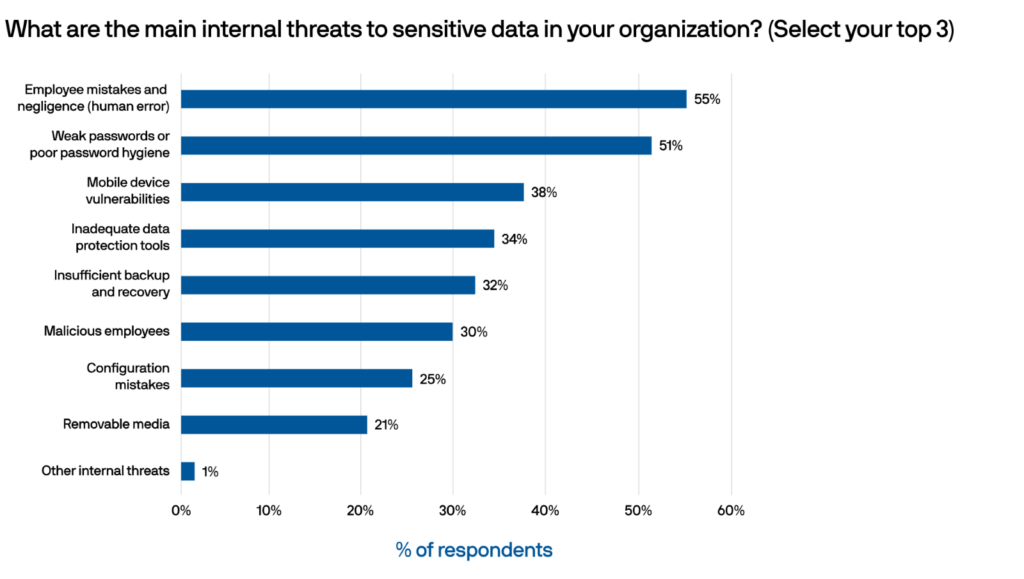
Based on answers from people in the workforce, the report reveals an alarming trend: a substantial 51% of reported data security threats were attributed to the usage of weak passwords or the neglect of proper password hygiene.
Weak passwords have become a gateway for cybercriminals to exploit, leading to many potential repercussions, including data breaches, financial losses, regulatory non-compliance, and severe damage to an organization’s reputation. This statistic paints a picture of the vulnerabilities that can be easily exploited by malicious actors seeking unauthorized access to sensitive information.
4 password security best practices
At the enterprise level, robust password security practices are essential to safeguard sensitive information, maintain regulatory compliance, and protect the organization from cybersecurity threats. By implementing these best practices and fostering a culture of cybersecurity awareness, businesses can significantly enhance their overall security posture.
1. Create secure passwords
Implement a policy that enforces the use of complex passwords, combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Encourage using passphrase-based passwords, which are longer and easier to remember while maintaining security.
Additionally, consider using password generators to create strong and unique passwords for each account and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
2. Regularly change and update passwords
Set a mandatory password change interval for all enterprise accounts, especially those with access to sensitive information. Regularly rotate passwords for service accounts, administrative accounts, and privileged access. Implement automated reminders to prompt employees to update their passwords within the designated timeframe.
3. Store and share passwords securely
Use a reputable enterprise-grade password management solution to store and manage passwords securely. Avoid sharing passwords through email or unsecured messaging platforms.
Instead, leverage secure password-sharing features password managers provide or use encrypted communication channels when necessary. Encryption can safeguard data even if password security is compromised by converting the information into an unreadable format that can only be deciphered with the correct encryption key.
4. Implement company-wide password policies and training
Develop a comprehensive password policy that outlines the requirements for password complexity, length, and expiration. Enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all accounts, particularly those with access to critical systems. Regularly review and update the password policy to align with evolving cybersecurity standards.
In addition, provide ongoing training to employees about password security, phishing awareness, and best practices for maintaining strong passwords.
Additional enterprise-level password security tips
The four best practices mentioned above only scratch the surface in terms of ways you can keep your data and information safe at the enterprise level. Some other tips and tricks include:
- Role-based access control (RBAC). Implement RBAC to assign appropriate levels of access to employees based on their roles and responsibilities. Limit access to sensitive data and systems to only those who require it.
- Privileged account management (PAM). Implement PAM solutions to tightly control and monitor access to privileged accounts. Use just-in-time access and session recording to enhance security and accountability.
- Single sign-on (SSO). Consider adopting SSO solutions to allow employees to use a single set of credentials to access multiple applications, reducing the need for multiple passwords.
- Password expiry notifications. Send automated notifications to employees before password expiration, ensuring they have sufficient time to update their passwords.
- Account lockouts and monitoring. Set up account lockout policies and monitor for suspicious activities, such as repeated failed login attempts, to identify potential security breaches.
Moreover, software like WinZip can facilitate robust password security for organizations by providing advanced encryption capabilities that protect files and archives with strong passwords, ensuring confidential data remains inaccessible to unauthorized users.
How to create a secure password
A strong password could be something like “Tr#9P$yx5L@vE!” and is created by combining several key elements:
- Length: Aim for a minimum of 12 characters. Longer passwords are generally more secure.
- Variety: Use a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters (e.g., !, @, #, $, %, ^, &).
- Avoid patterns: Don’t use easily guessable information like birthdates, names, or dictionary words.
- Use uncommon words or phrases: Create a passphrase by stringing together unrelated words, making it harder to guess.
- Misspellings and substitutions: Introduce intentional misspellings or substitutions, such as replacing letters with similar-looking numbers or characters (e.g., “L” with “1”, “E” with “3”, etc.).
- No personal information: Avoid using easily obtainable details like your name, username, or company.
Weak password examples
Weak passwords are not secure because they lack complexity, randomness, and uniqueness. They can be easily guessed using automated tools that try common words, phrases, and predictable patterns.
Moreover, these passwords are often the first choices attackers try when attempting to breach an account. Using weak passwords puts your personal information, accounts, and data at significant risk of being compromised.
Some examples of weak passwords include:
- Password123. This password is weak because it’s a common word followed by a predictable sequence of numbers. It’s easily guessable and vulnerable to dictionary attacks.
- 123456. This is one of the most commonly used passwords, consisting of a simple sequence of numbers. It offers no complexity or unpredictability.
- Qwerty. This password uses a simple keyboard sequence. Attackers often attempt such patterns because they are easy to guess.
- YourName123. Using personal information like your name and a basic number provides minimal security and is easily guessable.
- Letmein. This phrase is commonly used and easily guessable. Attackers are aware of such common choices and will try them.
- Birthdates. Using important dates makes it easier for attackers to crack your password through social engineering or online research.
While WinZip® Enterprise is primarily known as file compression and encryption software, it can also play a role in creating secure passwords. WinZip can assist in mitigating cyber threats via encryption and password protection methods, secure file sharing, and data loss prevention (DLP) software.
Try it now and learn how to safeguard your organization’s future from insider threats.
Download our survey today to learn more about your business’s data security threats.