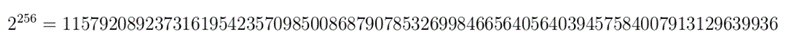Businesses of all sizes depend on cloud services to better manage their files and data. Different platforms provide various degrees of security, so data stored in the cloud might not be as secure as you think.
In fact, 70% of organizations that store data with major cloud vendors were hacked or experienced a data leak in 2020. The risk is even more significant for multi-cloud enterprises, who reported twice as many security incidents as organizations utilizing a single platform.
Encrypted cloud services offer an additional layer of protection against cyber threats and data breaches. This enables companies like yours to leverage the benefits of cloud connectivity without putting sensitive information at risk.
In this article, we explore the factors that make encrypted cloud services essential for your business and review four services including WinZip Enterprise® that keep your information safe.
Why encrypted services are key to cybersecurity
Almost all cloud services offer some form of encryption. It is up to you as the customer to ensure you understand a particular provider’s policies and procedures for encryption and encryption key management.
If your cloud provider fails to comply with federal, state, and local cloud security standards, laws, and regulations it can result in a multitude of negative ramifications. This may include penalties, fines, legal disputes, and other challenges that could be quite devasting to your business.
The encryption key is what codes (encrypts) and decodes (decrypts) the data. Without the correct key, you cannot transform ciphertext back into readable plain text. The average enterprise could have hundreds or thousands of encryption keys, each of which must be protected against unauthorized access and loss.
Most cloud services—91%—do not encrypt data at rest. If the provider experiences a breach, your organization’s data could be compromised. This is why it’s important to understand what protections your service providers have in place, including safeguards for data, whether it is in transit or at rest.
Today, more than 60% of corporate data is stored in the cloud. Cloud storage enables users to access data from anywhere—all they need is a network connection and authorization to access the files.
Without encryption, these cybercriminals can easily intercept your sensitive and confidential information. Once they have access to customer data, personally identifiable information (PII), intellectual property (IP), and other types of unencrypted cloud data, they can leverage it for financial gain, to commit fraud, or cause other types of harm.
Experiencing a data breach when valuable information is unencrypted can be devasting for businesses of all sizes. In addition to the costs involved in recovering lost data, there are additional factors that can negatively impact your organization’s bottom line. These factors can be classed into two broad categories:
Direct costs. Costs associated with responding to cybersecurity events are considered direct costs. Examples include operational disruption, regulatory fines, investigation costs, and settlements or reimbursements to affected parties.
Indirect costs. The resources spent recovering from a data breach are indirect costs. Examples include operational downtime, loss of customers’ confidence, reputational damage, and stagnated business growth.. Examples include operational downtime, loss of customers’ confidence, reputational damage, and stagnated business growth.
The benefits of encrypted cloud services
As companies adopt cloud services, the complexity of their data infrastructure increases, and the attack surface grows. Data exposure is the second-most common issue with cloud security, and encryption is key to safeguarding sensitive data in the event of a breach.
Various laws and regulations govern how businesses must protect sensitive information. However, these often do not apply to cloud service providers. For example, your service provider might not be subject to the same disclosure requirements in the event of a data breach. This is because your organization owns the data, which makes you legally responsible for the breach even if it is caused by the cloud service provider.
Fortunately, these data breach disclosure requirements also tend to include a safe harbor clause. This is a legal provision that removes the disclosure requirement so long as the stolen data is undecipherable to whoever steals it. As long as you have appropriate safety measures in place, such as encryption, your organization is protected from data breach litigation.
Leveraging encrypted cloud services for your business yields the following benefits:
Comprehensive data protection. File-level encryption adds authentication and security into every data file. In the event thatIf information is intercepted in transit, it remains encrypted and useless to cybercriminals. Any private, sensitive, or confidential information remains safe because malicious actors cannot steal or modify it.
Mitigation of insider threats. Whether through intentional actions or human error, insider threats can pose real harm to your data security. An encrypted cloud service adds additional layers of security that keeps data safe as it moves between users, devices, and systems. This is especially important for distributed and remote work environments, which are often targets of ransomware and firmware attacks.
Regulatory compliance. Encrypted cloud services offer advanced security elements, including data filtering, backup and recovery functions, policy-based data retention, and audit trail reporting. This protects critical data and adheres to various compliance requirements such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), and Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA).
Encrypted cloud services—four Examples
Encrypted cloud services come in all shapes and sizes. The best options for your business should have certain key features and functionalities, such as:
Compatibility with major cloud platforms. When choosing an encryption service, it is important to be able to manage and share files across the cloud environments in use at your organization.
Secure collaboration. Encrypted cloud services should enable faster, better workflows and equip teams to work collaboratively. With built-in layers of protection, you can share and collaborate on files without compromising sensitive data.
Multiple encryption layers. Different cloud services offer different degrees of encryption and security. Some only have one encryption layer, while others are customizable to your unique business needs.
Here is a list of four encrypted cloud services for your business:
1. Boxcryptor
Boxcryptor provides end-to-end encryption and is compatible with over 30 public cloud providers. It links to your local folders or cloud storage service and encrypts all the data within. Boxcryptor sets up a virtual drive within your file explorer, which is where you will find your encrypted data.
There is no option to filter or exclude certain file types, which means all files are automatically encrypted and decrypted. You must be logged in to your Boxcryptor account to decrypt and access data.
To enable file sharing, the recipient must also have a Boxcryptor account. Otherwise, you can use the solution’s Whisply integration to create customizable sharing links that are compatible with OneDrive, Google Drive, and Dropbox.
2. NordLocker
NordLocker leverages private cloud technology for its file encryption services. It does not offer direct integration with any cloud storage platform, which means you must set up the storage service on your device.
Encrypted data is stored in folders, which are called lockers. These lockers can reside on your local device or the NordLocker cloud. Anything stored in a NordLocker cloud is automatically synced with all your other NordLocker installations across your devices.
You can share folders (lockers) stored on your device, but you cannot share ones that are stored in the cloud. The recipient must also have a NordLocker account to access the shared files.
3. IDrive
IDrive gives you the ability to create your own encryption keys, giving you total control over your organization’s data security. Using and managing private key encryption requires additional technical expertise, which is why you can also use IDrive’s default encryption generation.
To utilize file sharing, you must select the default encryption option; you cannot share files protected by private encryption. IDrive offers a combination of cloud storage and backup functionalities, and all devices can be backed up into a single IDrive account.
IDrive does not delete data from backups, acting as a true archiving solution that keeps all backed up files in your IDrive account. Data stored in IDrive is protected using 256-bit AES encryption.
4. WinZip Enterprise
WinZip Enterprise® gives larger organizations military-grade data encryption, management, sharing, and compression within a single, customizable solution. It secures your company’s files in transit and at rest using 128- and 256-bit AES encryption, which means that you can customize your data protection level to match your industry’s unique requirements.
As a Windows Information Protection (WIP) enlightened solution, WinZip Enterprise gives IT admins the ability to separate business and personal data, as well as determine which users and applications can access specific datasets.
By finding and flagging duplicate files, WinZip Enterprise also helps organizations save thousands of dollars in data storage and management fees. It natively integrates with leading cloud storage providers, ensuring secure file management on any storage platform. WinZip Enterprise also enables teams to access internal and external files using its file zipping and unzipping capabilities.
WinZip Enterprise enables businesses to protect critical data, enforce protocols, and empower teams to collaborate on one centralized platform, simplifying operations. With WinZip Enterprise, organizations will be able to boost their productivity rates and optimize daily workflows, while keeping sensitive information secure.
Find out how WinZip Enterprise can protect your business’s privacy in the cloud.